
For Magic Water Elf Kits, manufacturers and trading companies serve fundamentally different roles.
Manufacturers own and control production facilities, offering stronger quality control, deeper customization, and better cost efficiency at scale.
Trading companies coordinate multiple third-party suppliers, providing flexibility and lower entry barriers but with reduced transparency and higher long-term costs.
Chapter 1: Core Differences in Supply Chain Positioning
The core difference between a Magic Water Elf Kit manufacturer and a trading company lies in production ownership and supply chain control.
A manufacturer owns and manages production facilities, including molding, bead expansion, assembly, and quality control. A trading company does not own factories and instead coordinates multiple third-party suppliers.
What Defines a Magic Water Elf Kit Manufacturer?
A true Magic Water Elf Kit manufacturer owns and controls the entire production process,
rather than merely coordinating it. This distinction is critical.
Manufacturers typically operate integrated facilities that include:
- Injection molding workshops (commonly 80–500 ton machines)
- Expansion bead production lines or exclusive chemical supply contracts
- Automated or semi-automated assembly lines
- Independent quality control laboratories
- Mold design, storage, and maintenance departments
Most qualified manufacturers are located in China’s established toy clusters,notably Chenghai (Guangdong) and Yiwu (Zhejiang).
These factories usually hold ISO 9001 certification and operate under standardized quality management systems.
From a procurement perspective, the key advantage of working with a manufacturer is vertical integration. Raw material selection, molding parameters,assembly standards, and final packaging are all controlled under one management system.
This reduces quality variance and allows faster corrective action when issues arise.
For example, when bead expansion inconsistency or pigment migration occurs,a manufacturer can trace the issue back to specific raw material batches within 24 hours. In contrast, indirect sourcing models often require multiple days of investigation and responsibility clarification.
Case Reference: OEM Customization
1. Application Example: Creative Play
2. Case Reference: OEM Customization
3. Procurement Decision Example
4. Cost Control Case
Understanding the cost structure is essential for budgeting. The Cost Breakdown for Sourcing Magic Water Elf Kits from China explains materials, packaging, shipping, and import fees in detail.
5. Quality Management Example
To ensure product safety and reliability, the Common Quality Issues in Magic Water Elf Kits and How Manufacturers Control Them shows real-world quality control measures applied by leading manufacturers.
6. Production and Customization Application
Learn how materials, production processes, and customization options affect product quality in the Magic Water Elf Kit Manufacturer: Production Process, Materials, and Custom Options.
7. Top Manufacturer Reference
If you plan to source directly, check out the Top 5 Magic Water Elf Kits Manufacturers for Kids in 2025 for reliable suppliers.
8. Choosing a Reliable Manufacturer Example
Use the How to Choose a Reliable Magic Water Elf Kit Manufacturer in China guide to evaluate credibility, production capacity, and compliance.
9. Bulk Order Evaluation Case
For large orders, the How to Evaluate a Magic Water Elf Kit Manufacturer for Bulk Orders explains supplier assessment and cost analysis for volume procurement.
10. Beginner Guide Application
New users can learn how to start with Magic Water Elf Kits via the What Is a Magic Water Elf Kit? Complete Guide for Beginners, covering gameplay, kit contents, and educational value.
Manufacturer Verification: How to Identify True Production Capability?
Distinguishing genuine manufacturers from intermediaries requires due diligence.
Critical verification steps include:
- Physical factory audits: Request video tours showing active production lines,not just warehouse facilities. True manufacturers will show molding machines with running production, not just assembled products.
- Technical depth assessment: Ask specific questions about ABS plastic shrinkage rates (typically 0.4-0.7%), expansion bead polymer chemistry, or pigment dispersion techniques.Manufacturers possess technical knowledge that trading companies often lack.
- Document verification: Examine business licenses for manufacturing scope,review export declarations showing factory of origin, and check ISO certifications that specifically mention production processes.
- Supply chain transparency: Genuine manufacturers can provide material safety data sheets (MSDS) from their raw material suppliers, not just finished product test reports.
What Is the Role of a Trading Company?
A trading company does not own production equipment or factories.Instead, it functions as a supply chain coordinator,connecting buyers with multiple upstream factories and service providers.
In the context of Magic Water Elf Kits, a trading company typically:
- Sources injection-molded parts from third-party factories
- Procures expansion beads from chemical suppliers
- Coordinates assembly and packaging workshops
- Handles export documentation, shipping, and customs clearance
The value of a trading company lies in operational convenience.For buyers with limited China sourcing experience, trading companies simplify communication, reduce supplier management complexity, and lower the initial learning curve.
However, this convenience comes at the cost of reduced transparency.Production schedules, material substitutions, and subcontracting decisions are often made without the buyer’s direct visibility.
Trading Company Tiers and Specialization Levels
Not all trading companies operate identically. The industry generally segments into three tiers:
- Basic Trading Agents: Small operations with minimal value addition beyond language translation and basic coordination. Typically add 15-25% margins with limited
quality control capabilities. - Specialized Trading Companies: Focus on specific product categories (toys,specifically water-based toys). Maintain dedicated QC teams, product development specialists,and have established relationships with multiple certified factories. Margins typically 8-15%.
- Supply Chain Solution Providers: Offer comprehensive services including inventory management, drop shipping, compliance consulting, and market intelligence.Function almost as external procurement departments. Margins 5-12% but offer significant operational efficiencies.
Chapter 2: Pricing Logic, MOQ, and Cost Transparency
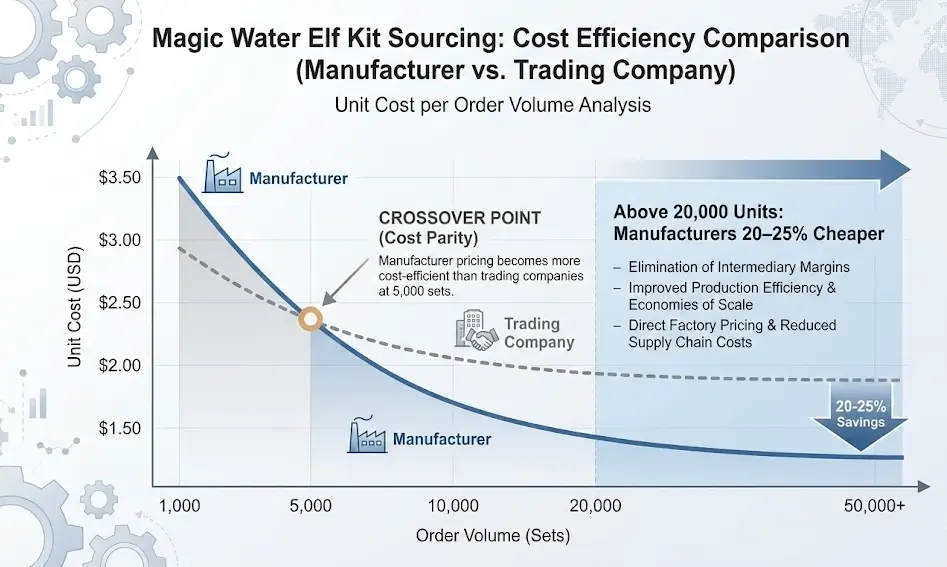
For Magic Water Elf Kits, manufacturers become more cost-efficient than trading companies once order volume exceeds 5,000 sets.
At volumes above 20,000 units, manufacturers are typically 20–25% cheaper due to the elimination of intermediary margins and improved production efficiency.
Manufacturer Pricing Structure Explained
Manufacturer pricing is typically based on a transparent cost structure.For Magic Water Elf Kits, a standard breakdown looks like this:
- Raw materials (ABS plastics, pigments, beads): 45–55%
- Labor and factory overhead: 25–30%
- Quality control and management: 10–15%
- Net profit margin: 8–12%
Because manufacturers eliminate intermediary layers, pricing becomes increasingly competitive as volume scales. Industry benchmarking across South China toy suppliers shows that:
- Below 1,000 sets: trading companies may appear cheaper
- 1,000–5,000 sets: pricing is often similar
- 5,000–20,000 sets: manufacturers are 10–18% cheaper
- Above 20,000 sets: manufacturers can be 20–25% cheaper
Manufacturers also offer value engineering options, such as optimizing material thickness, packaging formats, or assembly methods to reduce cost without compromising compliance.
Hidden Cost Considerations in Manufacturer Pricing
While manufacturer pricing appears straightforward, several hidden costs require consideration:
- Mold development fees: Ranging from $8,000 for simple single-cavity molds to $30,000+ for multi-cavity molds with complex detailing. Payment terms (full upfront vs.amortized across orders) significantly impact cash flow.
- Sample development charges: Typically $200-$500 per design iteration,though often credited against future orders.
- Testing and certification costs: While basic compliance testing is usually included, market-specific certifications (CE, ASTM, etc.) may incur additional charges of $1,500-$3,000 per product variation.
- Logistics and FOB terms Factory prices typically quoted as FOB (Free On Board) Chinese port. International shipping, insurance, and destination port charges add 8-15% to landed cost.
Trading Company Pricing Logic
Trading company pricing typically includes:
- Factory procurement cost
- Service margin (5–15%)
- Risk premium for new buyers (3–5%)
While this structure benefits small trial orders, it becomes increasingly inefficient for long-term, high-volume procurement.
The True Cost of Trading Company Services
Trading company margins are often justified through value-added services:
- Quality inspection services: Pre-shipment inspections typically cost $300-$500 per day for an experienced inspector.
- Communication and project management Bilingual staff coordinating between buyer and multiple factories saves significant management time.
- Risk mitigation: Trading companies absorb risks related to factory bankruptcies, production delays, or quality failures that individual buyers would struggle to manage directly.
- Logistics consolidation: Combining multiple small shipments reduces per-unit shipping costs by 15-30% compared to direct factory shipments.
MOQ Comparison and Strategic Implications
| Category | Manufacturer | Trading Company |
|---|---|---|
| Standard stock items | 3,000–5,000 sets | 100–500 sets |
| Modified packaging | 5,000–8,000 sets | 1,000–2,000 sets |
| New molds / ODM | 10,000+ sets | Usually unavailable |
For early-stage brands, trading companies provide flexibility.
For scaling brands, manufacturers provide sustainability.
Strategic Approaches to MOQ Challenges
Buyers can employ several strategies to navigate MOQ requirements:
- Product bundling: Combine multiple SKUs to meet manufacturer MOQs while maintaining product variety.
- Seasonal ordering: Consolidate orders for peak seasons rather than placing frequent small orders.
- Consignment inventory: Some manufacturers offer lower MOQs with consignment arrangements where they hold inventory until needed.
- Multi-buyer consolidation: Collaborate with non-competing buyers to combine orders, though this requires careful coordination.
Chapter 3: Customization, IP Protection, and Brand Control
Manufacturers offer deeper customization and stronger IP protection because mold ownership, material formulation, and production execution are centralized under one entity.
Trading companies often rely on shared molds and multiple subcontractors, which increases the risk of design leakage and unauthorized replication.
Customization Capabilities of Manufacturers
Manufacturers support deep OEM and ODM development, including:
- Bead size and expansion ratio customization
- Color saturation and pigment formulation
- Glow-in-the-dark, scented, or temperature-reactive beads
- Exclusive molds and 3D character designs
Mold development typically costs USD 8,000–30,000 and takes 6–10 weeks.Ownership terms can be contractually defined, providing strong IP protection.
Advanced Customization Opportunities
Beyond basic modifications, leading manufacturers offer sophisticated customization:
- Educational integration: Embedding educational elements like color mixingguides, science experiment instructions, or STEM learning components.
- Sustainability features: Biodegradable expansion beads, recycled plastic components, or plant-based pigments.
- Interactive packaging: QR codes linking to instructional videos,augmented reality experiences, or online communities.
- Accessory systems: Creating compatible accessory sets that work across multiple kits, building brand loyalty and repeat purchases.
Case Study: Successful Manufacturer Collaboration
A European educational toy company partnered with a Chenghai-based manufacturer to develop a patented “Magic Water Science Lab” series.
The 18-month collaboration involved:
- Joint investment of $45,000 in specialized molds
- Development of temperature-reactive beads that change color based on water temperature
- Creation of accompanying educational materials in 8 languages
- Exclusive production rights for 3 years with territorial restrictions
The partnership resulted in a product line that achieved €2.3 million in first-year sales
with 42% gross margins, significantly higher than industry averages.
IP Risks When Working With Trading Companies
Trading companies often rely on shared molds and multiple subcontractors.
This increases the risk of design leakage and unauthorized replication,
especially in competitive toy categories.
Specific IP Protection Strategies
Regardless of supplier type, implement these IP protection measures:
- Comprehensive NDAs: Cover not just final designs but also material specifications, production processes, and business terms.
- Mold ownership agreements: Clearly define ownership, storage rights,maintenance responsibilities, and destruction protocols.
- Component sourcing control: Specify approved material suppliers to prevent unauthorized substitutions that might compromise unique formulations.
- Regular factory audits: Conduct unannounced audits to verify production is limited to authorized quantities.
- Legal jurisdiction specifications: Ensure contracts specify dispute resolution in jurisdictions favorable to IP protection.
The Digital IP Challenge: 3D Scanning and Reverse Engineering
Modern technology presents new IP challenges. High-resolution 3D scanners can replicate physical products within hours. Protective measures include:
- Using proprietary material blends that cannot be easily reverse-engineered.
- Incorporating hidden design elements not visible in finished products.
- Implementing serialized packaging with authentication codes.
- Regular online monitoring for unauthorized replicas.
Chapter 4: Quality Control, Compliance, and Risk Management
Manufacturers provide more reliable quality control and compliance assurance because inspection is embedded across all production stages, not limited to final sampling.
Full compliance testing for major markets such as EN71 and ASTM typically costs USD 1,200–2,500 per product and requires 2–4 weeks.
Quality Control Execution Models
Manufacturers embed quality control into every production stage:
IQC (incoming materials), IPQC (in-process checks),and OQC (final inspection).
Advanced factories use GC-MS and ICP-MS testing to monitor chemical safety,ensuring compliance with global toy regulations.
Manufacturer QC Capabilities by Production Stage
| Production Stage | Key Quality Checks | Testing Equipment Used |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Receiving | Material certificates, color matching, bead expansion rate | Spectrophotometer, moisture analyzer, sieving machines |
| Injection Molding | Part weight consistency, flash examination, dimensional accuracy | Digital scales, calipers, CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machines) |
| Bead Production | Particle size distribution, expansion ratio, color uniformity | Laser particle analyzer, expansion test chambers |
| Assembly & Packaging | Component completeness, sealing integrity, labeling accuracy | Leak testers, barcode scanners, manual inspection stations |
Trading Company QC Limitations and Mitigations
Trading companies typically employ third-party inspection services with these limitations:
- Sampling limitations: Following AQL (Acceptable Quality Level) standards
means defects can be missed, especially with low-frequency but high-impact issues. - Process blindness: Inspectors see products at specific checkpoints but cannot monitor continuous production processes.
- Technical depth: Most inspectors verify appearance and function but lack equipment to test material composition or chemical safety.
Mitigation strategies when working with trading companies include:
- Requiring inspection reports from internationally recognized firms. (SGS, BV, TUV)
- Conducting pre-production material testing at accredited laboratories.
- Implementing progressive sampling where early production samples are tested before full production runs.
- Establishing clear rejection criteria and corrective action protocols.
Regulatory Compliance Coverage
- EU: EN71, REACH
- USA: ASTM F963, CPSIA, CPC
- Canada: SOR/2011-17
- Australia/NZ: AS/NZS ISO 8124
- Japan: ST 2016
Emerging Compliance Challenges
Recent regulatory developments impact Magic Water Elf Kit production:
- Microplastics regulation: EU’s restriction on intentionally added microplastics (October 2023) affects traditional expansion beads, driving demand for biodegradable alternatives.
- PFAS restrictions: Increasing limitations on per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in packaging materials and water-repellent coatings.
- Sustainability reporting: New requirements for environmental impact disclosure under EU’s CSRD (Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive) affecting larger buyers.
- Digital product passports: Proposed EU regulations requiring digital records of product composition, recyclability, and environmental impact.
Compliance Cost Analysis
Full compliance for major markets involves significant investment:
| Certification | Typical Cost | Validity Period | Testing Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| EN71 (Full Set) | $1,800 – $2,500 | Indefinite (for specific product) | 3-4 weeks |
| ASTM F963 | $1,200 – $1,800 | Indefinite (for specific product) | 2-3 weeks |
| CPC (CPSIA Compliance) | $800 – $1,500 | Annual renewal recommended | 2-3 weeks |
| REACH SVHC Screening | $400 – $800 per material | Until formulation changes | 1-2 weeks |
Chapter 5: Comprehensive Comparison & Decision Matrix
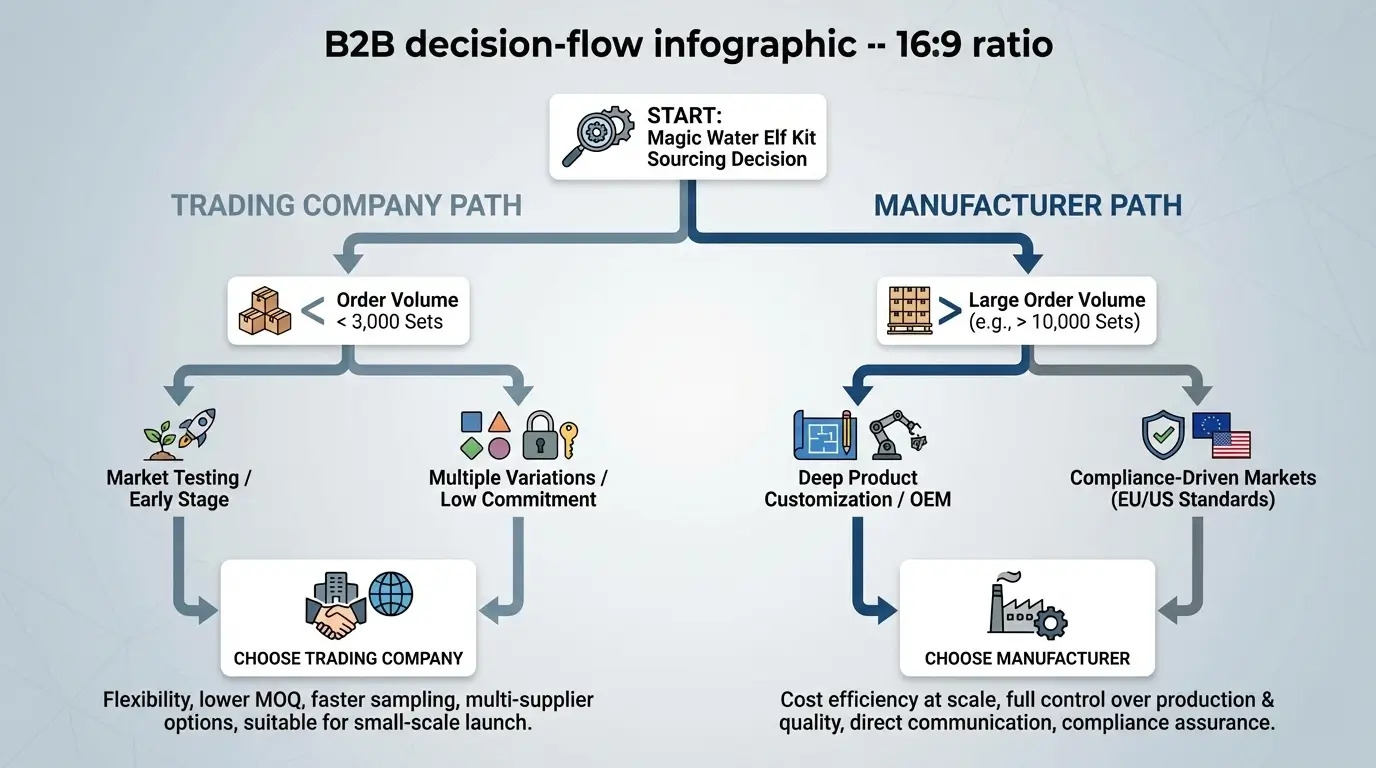
Choose a trading company for orders below 3,000 sets or for early-stage market testing with multiple product variations.
Choose a manufacturer for large volumes, deep customization, and brands targeting EU or US compliance-driven markets.
Step 1: Analyze Your Internal Requirements
- Annual purchase volume
- Customization level
- Target market compliance strictness
- Brand development stage
Develop a weighted scoring system for supplier selection:
| Criteria | Weight (1-10) | Manufacturer Score (1-10) | Trading Company Score (1-10) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit Cost at Target Volume | 9 | 9 | 6 | Based on 10,000+ unit orders |
| MOQ Compatibility | 7 | 5 | 9 | For orders under 3,000 units |
| Customization Depth | 8 | 9 | 4 | For new product development |
| Compliance Assurance | 10 | 9 | 7 | For EU/US markets |
| Communication Efficiency | 6 | 6 | 9 | For buyers without Chinese language skills |
| Risk Management | 8 | 7 | 8 | Trading companies offer multi-factory flexibility |
Step 2: Decision Flow Logic
- Below 3,000 sets → Trading company
- Deep customization required → Manufacturer
- EU/US markets → Certified manufacturer
- First-time sourcing → Trading company
- Strong QC capability → Manufacturer
Many successful companies implement hybrid approaches:
- Phase 1: Testing & Learning (Months 1-12): Use trading companies for market testing with multiple small-order variations. Focus on learning consumer preferences and identifying winning designs.
- Phase 2: Consolidation & Transition (Year 2): Shift best-selling items to manufacturers for cost optimization while maintaining trading company relationships for new product experimentation.
- Phase 3: Strategic Manufacturing Partnerships (Year 3+): Establish long-term agreements with 1-2 key manufacturers for core product lines, incorporating joint development and capacity reservation clauses.
A successful Amazon FBA seller of Magic Water Elf Kits followed this progression:
- Year 1: Started with trading company, testing 12 different designs with orders of 500-1,000 units each. Achieved $380,000 revenue with 28% gross margins.
- Year 2: Identified 3 top-performing designs. Transitioned these to a manufacturer with orders of 5,000+ units each. Revenue grew to $1.2M with margins improving to 35%.
- Year 3: Invested $25,000 in exclusive mold development with the manufacturer. Launched patented “Magic Water Planet” series. Revenue reached $3.1M with 42% margins and established brand recognition beyond Amazon.
Chapter 6: Future Trends and Strategic Implications
Future sourcing decisions for Magic Water Elf Kits will increasingly be influenced by sustainability regulations, digital traceability, and compliance transparency rather than unit price alone.
Technological Advancements Impacting Both Models
Several technological trends are reshaping the manufacturing and trading landscape:
- Digital twin technology: Virtual replicas of production processes allowing remote monitoring and optimization, reducing the need for physical presence.
- Blockchain traceability: Immutable records of material provenance,production conditions, and compliance documentation accessible to all supply chain participants.
- AI-powered quality inspection: Computer vision systems detecting defects with greater accuracy than human inspectors, available to both manufacturers and quality-focused trading companies.
- 3D printing for rapid prototyping: Reducing mold development time from weeks to days for design validation before committing to expensive steel molds.
Sustainability as a Differentiator
Environmental considerations increasingly influence sourcing decisions:
- Circular economy models: Some manufacturers now offer take-back programs for used products and recycling of expansion beads.
- Carbon footprint transparency: Progressive suppliers provide product-level carbon accounting, appealing to eco-conscious buyers.
- Water-based innovations: Development of expansion beads that biodegrade in water systems without microplastic pollution.
Geopolitical Considerations
Global trade dynamics impact sourcing strategies:
- China Plus One strategies: Many buyers maintain Chinese suppliers while developing secondary sources in Vietnam, India, or Mexico for risk diversification.
- Tariff engineering: Careful product classification and sourcing adjustments to minimize import duties in target markets.
- Regional trade agreements: Leveraging agreements like RCEP (Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership) for preferential tariffs when sourcing from Asia.
Manufacturer vs Trading Company Is a Strategic Choice
Choosing between a Magic Water Elf Kit manufacturer and a trading company is not simply about price. It is a strategic decision about control,risk management, and long-term brand value.
Manufacturers offer scalability and transparency. They enable deep customization,direct quality control, and sustainable cost advantages at scale.
The manufacturer path requires greater initial investment in relationship building, technical understanding, and potentially higher MOQs, but delivers superior long-term value for serious brands and volume buyers.
Trading companies offer flexibility and speed. They lower entry barriers,simplify communication, and provide valuable risk diversification through multi-factory networks. The trading company path suits market testing,smaller orders, and companies with limited sourcing experience or resources.
The most successful procurement strategies often evolve over time, beginning with trading companies for learning and validation, then transitioning to manufacturers for scaling and optimization.
The key is matching your supplier type to your specific business requirements, capabilities, and growth stage.
Regardless of path, successful sourcing requires diligence: verify capabilities,establish clear contracts, implement robust quality control, and build relationships based on transparency and mutual benefit. In the dynamic world of toy manufacturing,your supplier relationships can become your most valuable competitive advantage.
Final Recommendation Framework:
- For startups and test marketers: Begin with specialized trading companies. Focus on learning, flexibility, and risk management.
- For growing brands (50k+ annual revenue): Develop hybrid approaches.Maintain trading relationships for new products while transitioning bestsellers to manufacturers.
- For established brands (500k+ annual revenue): Prioritize direct manufacturer relationships. Invest in exclusive developments and strategic partnerships.
- For all buyers: Continuously assess supplier performance, stay informed about regulatory changes, and maintain flexibility to adapt as your business and the market evolve.
Trust, but verify—then build relationships that create value for all parties.
